AARP Hearing Center
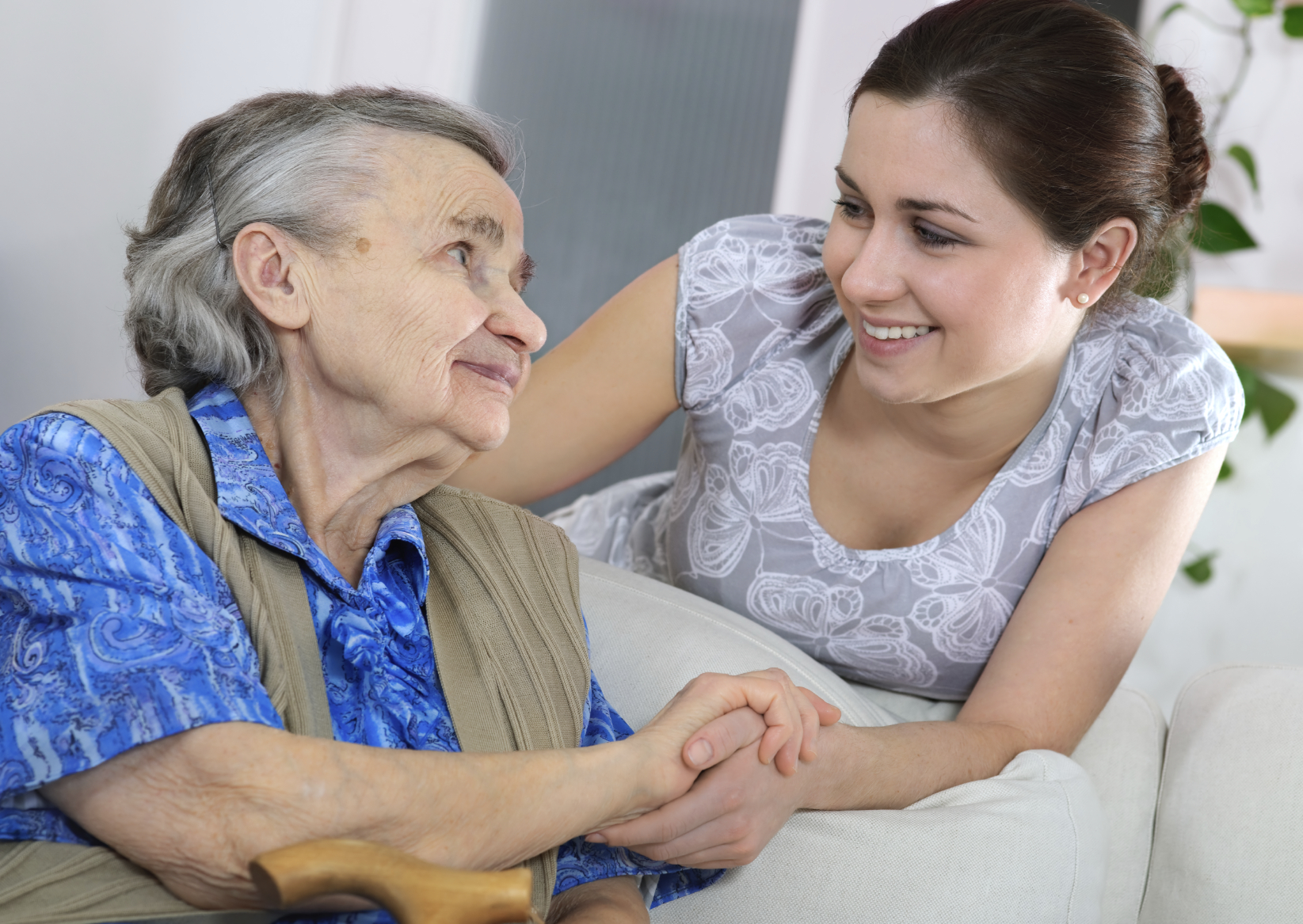

AARP’s new Long-Term Services and Supports (LTSS) Scorecard finds that more than three years after the COVID-19 pandemic began, care provided in the United States for older adults and people with disabilities is painfully inadequate. The report finds that major gaps persist in every state, including Pennsylvania, especially related to providing support for family caregivers, affordability and access, and the safety and quality of long-term services and supports.
Ranking #21 in the country, Pennsylvania has made progress to improve care options for older adults, including the use of Aging and Disability Resource Center/No Wrong Door Functions to connect older adults and persons with disabilities with supports and services in their community and home health aide supply. However, the report shows there is still much more to be done to keep up with the rapidly changing needs of an aging population.
“The pandemic reinforced the need to strengthen long-term care for countless loved ones across the country, including in Pennsylvania,” said Bill Johnston-Walsh, AARP Pennsylvania State Director. “Pennsylvania’s current pursuit of developing a Master Plan for Older Adults as a vehicle to transform the state’s services and supports infrastructure for older adults and persons with disabilities in Pennsylvania is incredibly promising. The Scorecard shows that there are many roads to travel before we meet the needs of all Pennsylvanians who deserve the very best care, including our state's 1.5 million family caregivers. It’s time to accelerate our efforts, for the sake of saving more lives.”
Additional key findings from the report include:
Home and Community-Based Services
There has been a surge in older adults receiving long-term care at home, rather than in nursing homes and other institutions. For the first time, more than half (53%) of Medicaid LTSS spending for older people and adults with physical disabilities went to Home and Community-Based Services (HCBS). This is up from 37% in 2009. HCBS includes support for home health care aides, respite services, assistive technology and home modifications and other services.
The average annual per-person cost of home care in 2021 was $42,000.
Nursing Homes and Institutional Care
Nationally, only 22% of nursing home residents live in a facility with a 5-star rating, and some races/ethnicities are less likely to live in a 5-star facility than others; about 5.7% of Pennsylvania’s nursing home residents live in a 5-star facility. Gaps in workforce and equity result in persistent problems in care. For instance, about 10% of nursing home residents nationwide experienced a pressure sore. Pressure sores can be life-threatening, leading to bone or joint infections, cancer, and sepsis.
Only nine states, including Pennsylvania, have enhanced hazard mitigation plans for natural disasters and other emergencies to systematically address the needs of vulnerable older adults and people with disabilities, including for nursing home residents.
“COVID-19 tested our long-term care systems, and they failed. Now is the time to take the lessons we’ve learned to fix them, for the sake of saving lives,” said Susan Reinhard, Senior Vice President, AARP Public Policy Institute. “AARP’s LTSS Scorecard shows some progress and innovation, but there’s still a long way to go before we have systems that allow people to age well and independently for as long as possible and support the nation’s 48 million family caregivers. It’s also clear some emerging issues deserve more attention – from whether nursing homes are prepared to confront natural disasters, to whether they have plans in place to maintain and grow their workforces.”
Recommendations
Key recommendations from the report and AARP to strengthen support for long-term care and aging at home:
- Prioritizing saving time, money, and increasing support for the 48 million family caregivers, who are the backbone of the long-term care system, providing over $600 billion in unpaid care, such as with paid leave, tax credits, and other mechanisms to address health and financial needs.
- Investing in all aspects of Home and Community-Based Care infrastructure, such as increasing support and training for home health aides and home visits, supporting the ability to access and use medical devices and equipment, and updating key Medicaid regulations and payment models.
- Bolstering the nursing home and in-home care workforce, with improved recruitment and training, increasing pay, and expanding the ability of trained nurses, aides, community health workers and other paraprofessionals to take on some aspects of care. States can choose to enact and enforce staffing and related care standards.
- Expanding the use of innovative, effective models for nursing homes can improve both quality of care and quality of life, such as with smaller facilities and private rooms.
- Addressing inequities by investing to close the staggering gaps in access to quality care and facilities and staffing shortages.
- Building multisector plans for aging, coalitions and age-friendly health systems, and consider the wider needs to allow individuals to live independently in their homes and communities, such as having affordable and accessible housing and transportation, improved community design, and comprehensive emergency preparedness plans.
- Advancing innovation in cities, counties and states by supporting comprehensive state- and community-wide aging plans and piloting new approaches and programs, like Green House® Nursing Homes and presumptive eligibility, that can then be scaled.
- Ensuring every state in the nation has a sound emergency preparedness plan to support nursing home residents, particularly in times of crisis – including natural disaster.
The Scorecard includes a series of 50 indicators focused on 1) affordability and access; 2) choice of setting and provider; 3) safety and quality; 4) support for family caregivers; and 5) community integration, using data from a variety of publicly available sources, such as the Centers for Medicaid and Medicare Services, American Community Survey, and Bureau of Labor Statistics.
The LTSS Scorecard is funded by AARP Foundation with the support of The SCAN Foundation, The Commonwealth Fund, and The John A. Hartford Foundation and has been updated every three years since 2011.
"Every person, regardless of where they live, their race, or their socioeconomic background, deserves long-term care that is accessible, safe, and prioritizes what matters most to them,” said Terry Fulmer, PhD, RN, FAAN, president of The John A. Hartford Foundation. “The Scorecard shows that there are significant regional and racial disparities in the care a person receives. State policymakers can and should take steps now to close the gap in access to quality care.”
"The LTSS Scorecard indicates progress in some state programs, but opportunities exist for both public and private sectors to enhance LTSS,” said Sarita A. Mohanty, MD, President and Chief Executive Officer of The SCAN Foundation. “Most older adults prefer home and community-based care that meets their needs, but it remains financially out of reach for many working-class families, particularly those who are part of the 'forgotten middle'. TSF is committed to identifying, highlighting, and elevating innovative policies and programs to ensure all older adults can age well in home and community."
“Equity is an essential component of high-quality health care, and is especially important in LTSS,” said Melinda Abrams, Executive Vice President, Programs, The Commonwealth Fund. “I am thrilled AARP was able to add race and ethnicity data for several indicators. This year and going forward, this new data will shed light on the experiences people of color in LTSS and draw attention to individuals with the greatest need.”
To view the full Scorecard and state-by-state information visit www.ltsschoices.aarp.org.
State Rankings:
· Tier One: 1: Minnesota; 2: Washington state; 3: District of Columbia; 4: Massachusetts; 5: Colorado.
· Tier Two: 6: New York; 7: Oregon; 8: Hawaii; 9: Vermont; 10: New Jersey; 11: California; 12: Rhode Island; 13: Connecticut; 14: Maryland; 15: Wisconsin; 16: Maine.
· Tier Three: 17: Delaware; 18: Nebraska; 19: North Dakota; 20: New Mexico; 21: Pennsylvania; 22: Arizona; 23: Iowa; 24: New Hampshire; 25: Illinois; 26: Alaska; 27: Indiana; 28: Virginia; 29: Utah; 30: Kansas; 31: Michigan; 32: Ohio; 33: Montana; 34: Texas; 35: Idaho.
· Tier Four: 36: South Dakota; 37: Arkansas; 38: Missouri; 39: Georgia; 40: Wyoming; 41: North Carolina; 42: Kentucky; 43: Florida: 44: Nevada; 45: Louisiana; 46: Oklahoma.
· Tier Five: 47: Tennessee; 48: Mississippi; 49: South Carolina; 50: Alabama; 51: West Virginia.